
Optical Testing Instruments
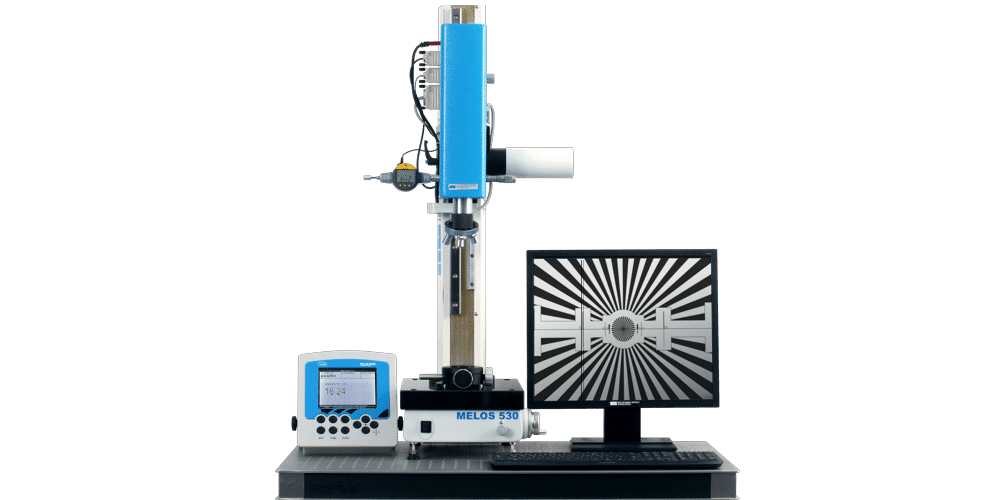
Measuring Equipment for Optical Systems: MELOS 530
Measuring Equipment for Optical Systems: MELOS 530
Product description
The measuring combination for lenses and optical systems MELOS 530 is the best solution for the comfortable and fast determination of effective focal length, back focal length, radii as well as wedge angles.
MELOS 530
Product advantages
- Fast switching between the different measuring modes. Due to an improved design, no time-consuming change of the measuring system is required.
- Direct reading of the measurement results on a stand-alone display unit. All calculations necessary for the evaluation of the negative and positive focal length measurement are performed by the display unit. The results can be stored in a table and transferred to a computer for documentation purposes at a later time. During the measurement process, the user is supported by the integrated help function. It allows even the inexperienced user to quickly get familiar with the usage of the instrument.
- Precise adjustment of the image planes through display of the reticle image on the monitor.
- Full control over the measurement process by manual adjustment.

Typical Applications
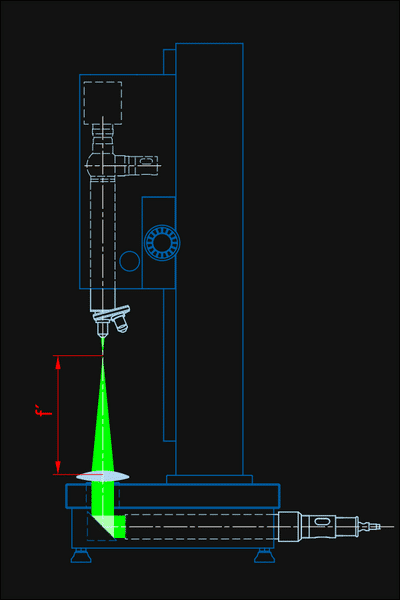
Measurement of Positive EFL
The measuring collimator projects a reticle image to infinity. The specimen produces image of the reticle in its focal plane. The size of the reticle image is determined solely by the known focal length of collimator objective and the focal length of the specimen, which is to be measured. The measurement of the size of the projected reticle with a reading telescope consisting of an autocollimator and an attachment achromat gives the focal length. The measurement process is done menu-controlled by the display unit. For measurement of positive focal lengths the combinations 1, 2, 3, 4 can be used.
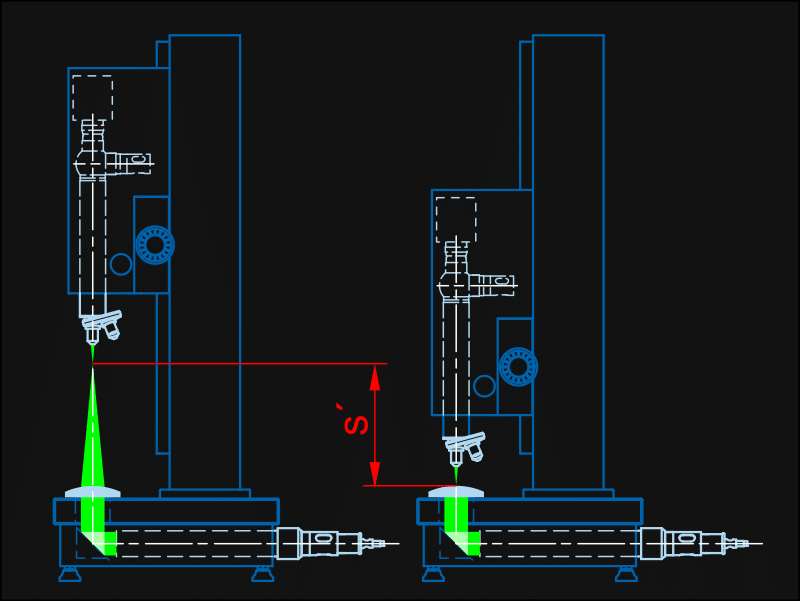
Measurement of Negative EFL
The measuring collimator projects a reticle image to infinity. The specimen produces a virtual image of the reticle in its focal plane. The measurement of the size of the virtual reticle image with a reading telescope consisting of an autocollimator and an attachment achromat gives the focal length. The measurement process is done menu-controlled by the display unit. For measurement of negative focal lengths the combinations 2, 3, 4 can be used.
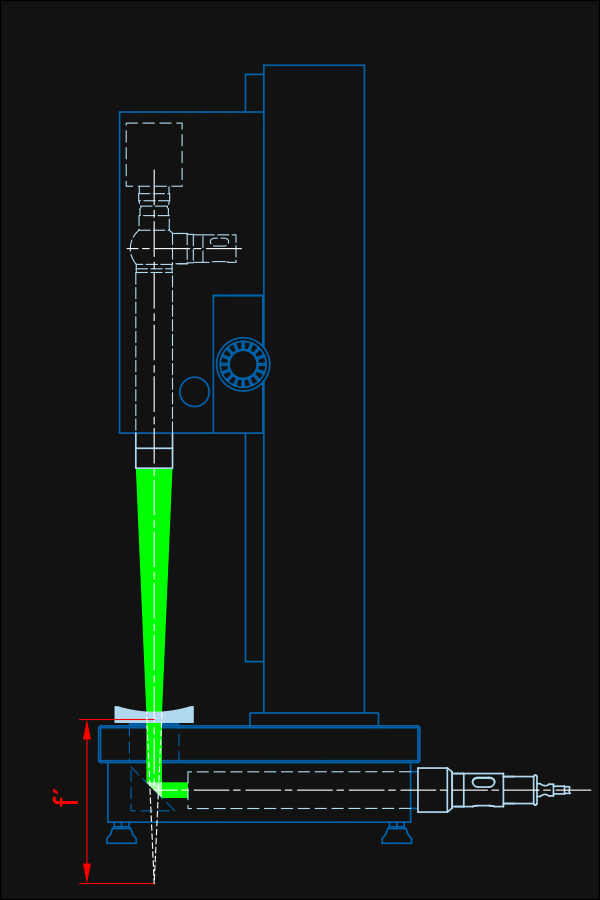
Measurement of BFL
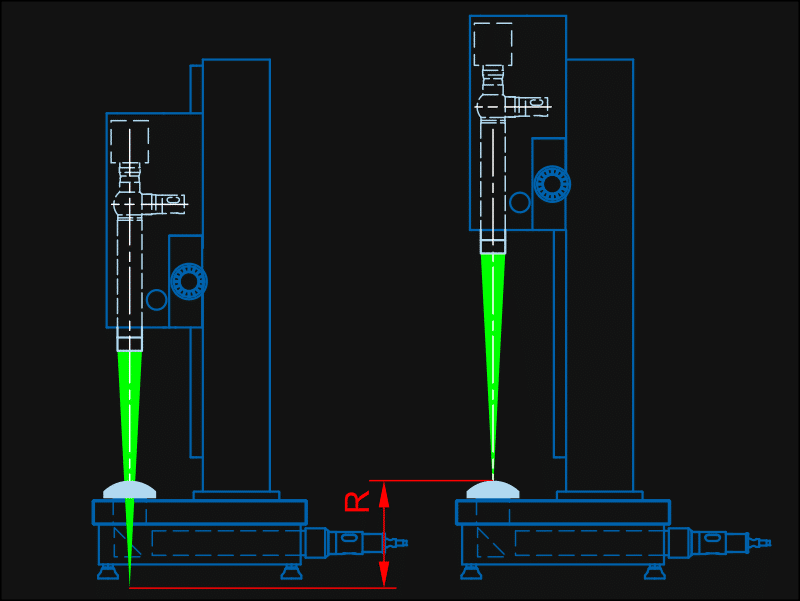
Measurement of Convex and Concave Radii
An autocollimator with attachment achromat is used. The autocollimator produces a reticle image in the focal plane of the attachment achromat. This configuration produces autocollimation images in the vertex and centre of curvature of the surface of the specimen. The vertical distance R is the radius, which is to be measured. The measurement process is done menu-controlled by the display unit. For measurement of convex and concave radii the combinations 3, 4, 6 can be used.
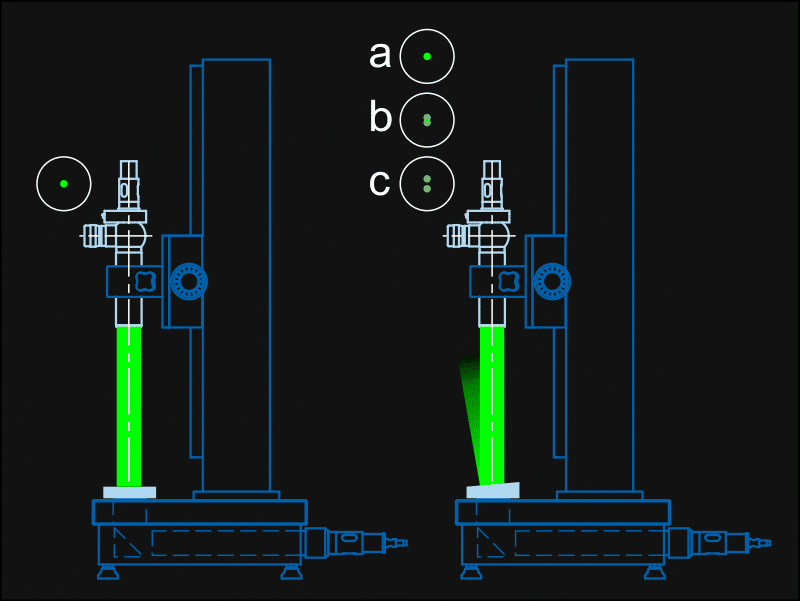
Testing of Wedge Angles and Parallelism
An autocollimator with a reticle turret is used. The autocollimator is equipped with a set of six pinholes. Each pinhole represents a certain wedge angle. The parallel beam from the autocollimator is reflected at both surfaces of the speciment. Each reflection produces an autocollimation image. If both pinhole images coincide (a) the surfaces are parallel. Otherwise a double image occursd. The wedge angle can be inside (b) or outside (c) the tolerance limit defined by the pinhole. For testing of wedge angle and parallelism the combinations 4 und 7 can be used.

